Colonization of oral
surfaces by Candida spp. is considered a risk factor for invasive fungal
infections. Oropharyngeal candidiasis manifests clinically as acute
pseudomembranous, acute atrophic, chronic atrophic, chronic hypertrophic/hyperplastic
and angular cheilitis.
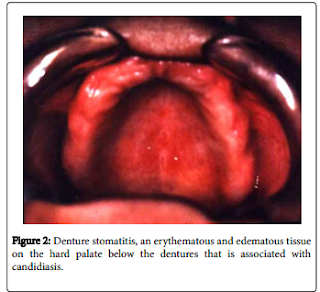
Denture-related stomatitis (or chronic atrophic
candidiasis) is characterized by an inflammation of the mucous membrane located
beneath the prosthesis, particularly under the upper denture, sometimes
accompanied by hemorrhagic petechiae. Denture stomatitis is the commonest form
of oral candidiasis and its reported prevalence varies widely reaching up to
65% of denture wearers. Patients may complain of a burning sensation,
irritation, discomfort, bad taste and disturbance of salivation, but in the
majority of cases they are unaware of the problem. Read more>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>
No comments:
Post a Comment