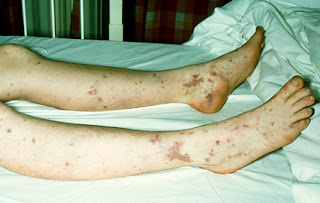
Malaria is a life threatening disease caused by
infected Anopheles mosquito bites. Control mainly depends on early diagnosis
followed by treatment with anti-malarial drugs. However, the treatment is severely hampered because of
spread of drug resistant malaria parasites. Recently drug named DDD107498 beendeveloped and about to enter human trials with all properties of potentialmalaria drug. The properties include (i) it shows effect on multiple species of
malaria parasites at several lifecycle stages, (ii) single dose effectiveness,
(iii) Active gametocyte clearance,(iv) good pharmacokinetics all these
characters proved this drug as a new- generation anti-malarial drug.
parasite, although it shows poor
physicochemical properties.
The research team further optimized the compound to
attain drug-like properties through cycles of design, synthesis and testing.
The significant optimization process included (i) Replacement of Bromine with
Florine to reduce molecular mass and lipophilicity, (ii) Replacement of the
3-pyridyl substituent with an ethyl-pyrrolidine group and (iii) Addition of a
morpholine group via methylene spacer. The final compound generated was named
as DDD107498, and was experimented both in-vitro, in-vivo and ex-vivo methods
using humanized mouse model and other model organisms against P.falciparum, P.
vivax and P. berghei to confirm its efficacy. The compound was further
evaluated for its drug-like properties, mode of action and safety measures. A
comparative study with presently available drugs was also done to confirm its
better efficacy, unique mechanism of action and ability to act at multiple
stages of the parasite life cycle. Read more............